In this article, let us see about the electric motor, the principle of the electric motor, the working of the electric motor, and its uses of electric motor.
What is Electric Motor ? Electric Motor is a device that converts the electrical energy given as input into mechanical energy as an output.
Input = " Current "
Output = " Rotational Movement "
Principle of Electric Motor
Principal of Electric motor ? The principle of the electric motor is defined as when we place a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field, the conductor expresses a mechanical force. The mechanical force will cause rotational movement in the conductor. So, we get a rotational movement from the motor as an output. The direction of rotation of the motor is determined by Fleming's left-hand rule.
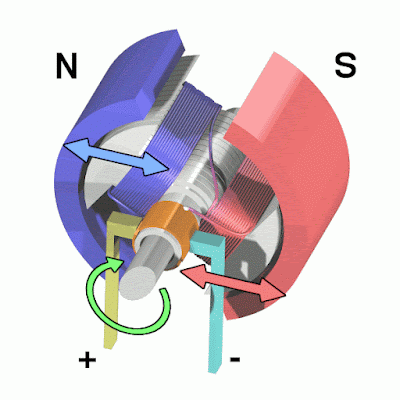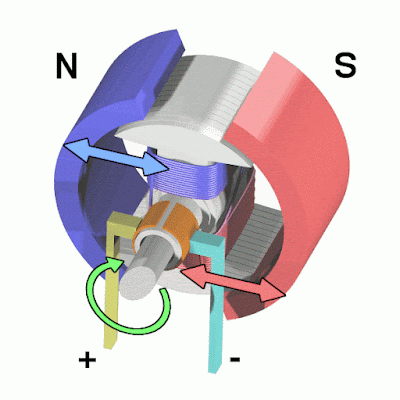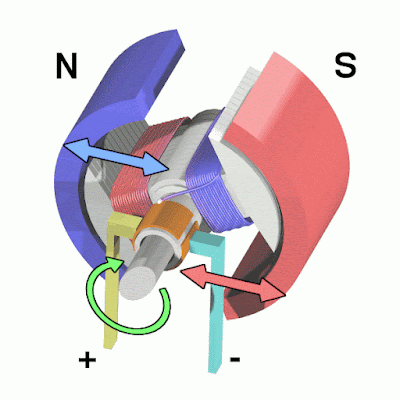 |
| Animation showing operation of a brushed DC electric motor | Image by Abnormaal, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons |
Working of Electric Motor
Working of electric motors ? In the motor, there are two magnetic poles in the area called Stator. The stator will not make any movement it is present in the inner layer of the motor. A conductor is placed in between these two poles. A power supply is given to the conductor using the brushes which are attached to the commutator at the end of the conductor. When we place the current-carrying conductor between the two magnetic poles, a mechanical force is developed in the conductor. Let's see how the mechanical force is developed in the conductor.
There exist two magnetic fields in the motor. 1. Magnetic field of the Magnetic Poles. 2. Magnetic field of the current carrying conductor. The direction of the magnetic field of the magnetic poles is from the north to the south pole. The magnetic field for the conductor is formed by the current flowing in the conductor. Now the conductor acts as an Electromagnet. The direction of the magnetic field of the current-carrying conductor is in a clockwise direction.
On the right side of the conductor, as both fields are in the same direction, the field strength is more and bent around the conductor. Whereas on the left side of the conductor, since both fields are in opposite directions, the field strength is less. Hence the resultant field exerts a mechanical force on the conductor from right to left. If the conductor is allowed to move, it will move from right to left due to this mechanical force.
Due to the mechanical force, the conductor moves from right to left and completes the 180° degree rotation. After completing the 180° degree rotation, the polarity of the conductor is automatically changed by the commutator which is attached at the end of the conductor. Again the field strength is more on the right side of the conductor. So, a mechanical force is developed on the right side of the conductor. Then, the conductor moves from right to left and completes another 180° degree rotation. Again the polarity of the conductor automatically changed. This process will continue until there is a power supply to the conductor which makes the conductor rotate. The rotating part in the motor is called as Rotor. Hence, we get a rotational movement from the motor as an output.
Uses of Electric Motor
- Electric Motor is used in
- Drilling Machine
- Washing Machine
- Water Pumps
- Fans etc.
- Electric Motor is used as Generator.


Post a Comment